Maternal mortality in the U.S. has become a growing public health concern, with recent studies revealing alarming trends in pregnancy-related deaths that continue to rise. As the nation leads its high-income peers in maternal mortality rates, it is crucial to address the underlying causes fueling this crisis, including significant maternal health disparities across different racial and ethnic groups. Over 80 percent of these pregnancy-related deaths are deemed preventable, highlighting the urgent need for improved access to prenatal and extended postpartum care. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on pregnancy has further exacerbated these challenges, making it imperative to strategize effective interventions to support at-risk populations. Experts indicate that cardiovascular diseases are increasingly becoming the leading cause of pregnancy-related mortality, underscoring the necessity for comprehensive healthcare solutions that prioritize maternal well-being.
The rising rate of maternal mortality in the United States, characterized by preventable pregnancy-related fatalities, has surfaced as a critical issue that demands immediate attention. This phenomenon highlights the need for enhanced maternal health care, particularly as numerous studies unveil mounting disparities in health outcomes among diverse communities. Issues stemming from inadequate postpartum resources and the lasting effects of COVID-19 are becoming increasingly apparent, which poses a heightened risk for vulnerable populations during and after pregnancy. Additionally, complications related to cardiovascular disease have emerged as a significant threat to maternal well-being, necessitating a robust and inclusive approach to healthcare during pregnancy. As awareness grows regarding the systemic barriers contributing to these trends, a comprehensive understanding of the factors influencing pregnancy outcomes becomes essential.
The Alarming Increase in Maternal Mortality in the U.S.
The United States continues to lead high-income countries with its disturbingly high maternal mortality rate, which has seen a significant rise in recent years. According to the latest studies, the maternal mortality rate climbed to 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births by 2022, marking the sharpest increase in 2021. This surge is primarily attributed to various systemic issues within the U.S. healthcare system, including a combination of factors such as inadequate access to prenatal and postpartum care, ongoing health disparities among racial and ethnic groups, and the pressures placed on healthcare resources during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Despite advancements in medical technology, over 80 percent of these pregnancy-related deaths have been deemed preventable. The health disparities are glaring, with American Indian and Alaska Native women facing mortality rates nearly four times higher compared to their white counterparts. This inequity highlights the urgent need for targeted interventions to alleviate these disparities and improve maternal health outcomes for all women in the U.S.
Understanding Pregnancy-Related Deaths in the Context of Maternal Health Disparities
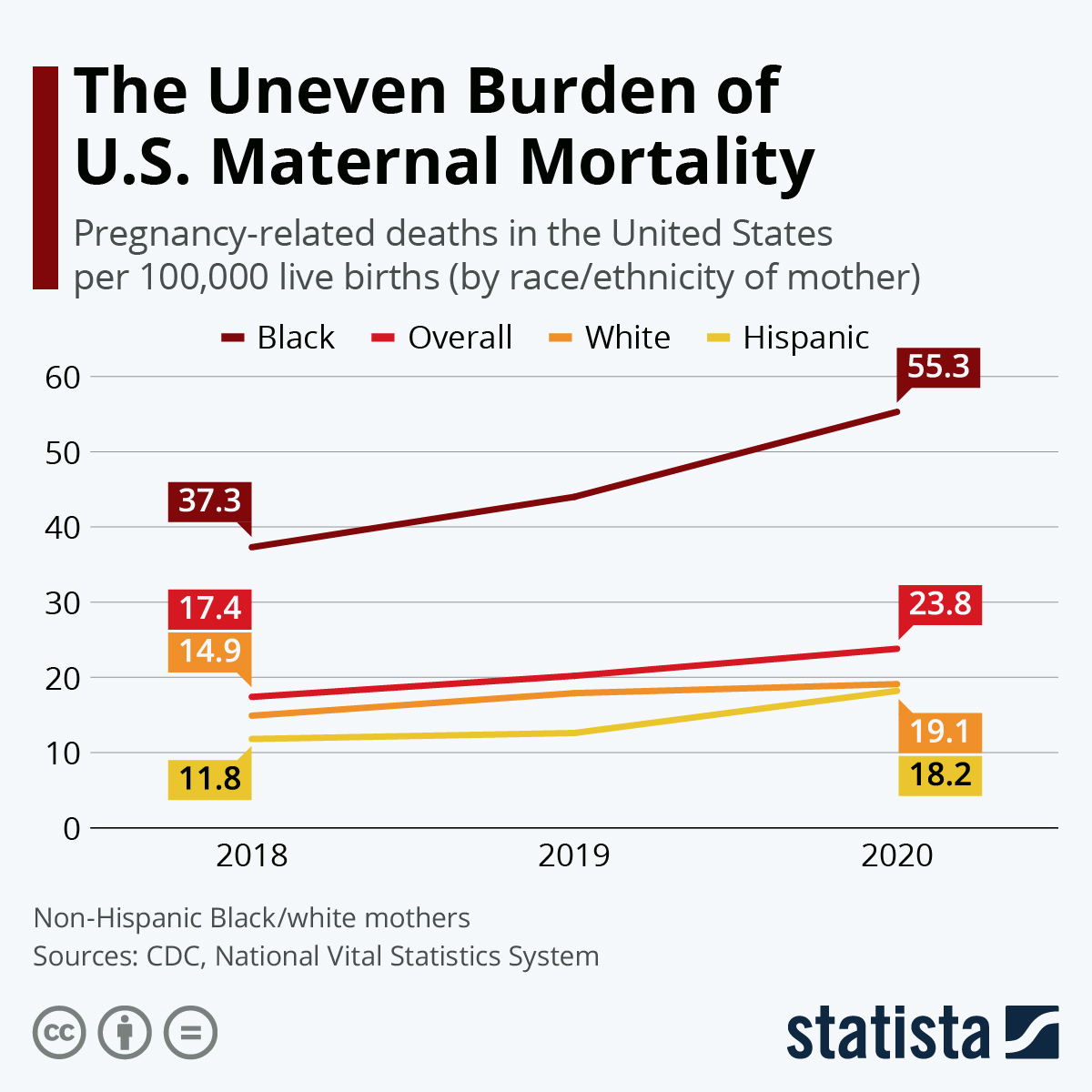
Maternal health disparities continue to plague the United States as evident in the statistics surrounding pregnancy-related deaths. These fatality rates reflect deep-rooted inequities based on race and socioeconomic status. The study found that non-Hispanic Black women faced a pregnancy-related mortality rate of 76.9 per 100,000 live births, emphasizing the crucial need for systemic reforms. Addressing these disparities requires an overhaul of the existing healthcare policies, ensuring equitable access to quality healthcare for marginalized communities.
Moreover, the differential in state-level maternal deaths further complicates the landscape of maternal health in the U.S. Some states report astonishingly high numbers, prompting the question of what effective measures are being implemented in places with better health outcomes, such as California. Understanding these state-specific approaches could provide a roadmap for reducing maternal mortality rates nationwide.
The Impact of Postpartum Care on Maternal Mortality Rates
One key finding in recent studies is the alarming rate of late maternal deaths, defined as those occurring between 42 days and one year postpartum. Nearly one-third of maternal deaths fall into this category, prompting new calls for a reevaluation of healthcare structures designed to support women in their postpartum journey. Traditionally, the healthcare focus has been on the six-week postpartum visit, leaving a gap in continuous care that could prevent preventable deaths.
Postpartum care must evolve into a continuous model that provides support and monitoring well beyond the initial weeks after childbirth. By emphasizing a more holistic view of maternal recovery, health professionals can address issues that lead to complications such as cardiovascular disease and other chronic health concerns, which are critical during this vulnerable stage.
Exploring the COVID-19 Impact on Pregnancy and Maternal Health
The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound impact on maternal health, contributing to a spike in pregnancy-related deaths. Studies indicate that the healthcare system’s focus shifted dramatically during the pandemic, often at the expense of proper and timely maternal care. With increased hospitalizations and resource allocation directed towards managing COVID-19 cases, expectant mothers have experienced disruptions in their prenatal and postpartum care, leading to heightened risks during pregnancy.
Additionally, the pandemic has exacerbated existing maternal health disparities, particularly among racial and ethnic minorities who already faced challenges accessing healthcare services. The combination of increased stress, anxiety, and physical health complications associated with COVID-19 underscores the urgent need to reassess and improve maternal healthcare systems to ensure safety and support for all mothers during any health crisis.
Addressing Cardiovascular Disease as a Leading Cause of Maternal Death
Cardiovascular disease has emerged as the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S., accounting for over 20 percent of fatalities. This trend signals a need for heightened awareness and targeted strategies to identify and manage cardiovascular health issues during pregnancy. With rates of chronic hypertension rising among younger populations, the inherent risks during pregnancy cannot be understated, necessitating effective monitoring and intervention strategies.
The implications of cardiovascular health extend beyond pregnancy, as the onset of pregnancy-related conditions such as preeclampsia can lead to long-term health issues. Therefore, integrating cardiovascular health screenings and education into prenatal care could potentially reduce maternal mortality rates and encourage healthier outcomes for both mothers and their newborns.
The Importance of Systematic Data Tracking in Maternal Health
The U.S. only implemented a systematic tracking system for maternal deaths in 2018, complicating efforts to assess and address the issue of maternal mortality comprehensively. The recent research, which began leveraging this new tracking system, highlights significant historical gaps in data, revealing the urgency of having accurate, timely information to inform policies and interventions aimed at reducing pregnancy-related deaths.
As data tracking improves, it enables healthcare professionals and policymakers to identify trends, understand disparities, and measure the effectiveness of interventions. Greater investment in data infrastructure is critical for monitoring maternal health outcomes and ultimately fostering a healthcare environment that prioritizes the well-being of mothers and infants.
Innovative Solutions to Improve Maternal Healthcare Outcomes
Addressing the rising rates of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. requires innovative solutions that extend beyond traditional care practices. Stakeholders must prioritize investments in comprehensive maternal healthcare, particularly during prenatal and postpartum stages. Solutions such as increasing healthcare access for underserved communities and implementing community-based programs can significantly impact maternal health outcomes.
Furthermore, healthcare providers must adopt a more patient-centered approach to care, fostering open communication and addressing the unique concerns of each individual. By tailoring healthcare interventions and resources to meet diverse needs, we can improve the effectiveness of maternal healthcare systems and significantly reduce the preventable nature of maternal mortality.
Promoting Public Awareness Around Maternal Health and Mortality
Public awareness campaigns focused on maternal health and maternal mortality are essential to garner support for systemic reforms in healthcare. Drawing attention to the shocking statistics surrounding pregnancy-related deaths can galvanize community engagement and advocacy efforts aimed at creating policy changes that prioritize maternal health.
Educating the general public about the importance of comprehensive prenatal and postpartum care can empower expectant mothers and families to seek necessary medical support. This proactive stance towards maternal health can lead to more informed birthing experiences and ultimately contribute to reducing the rates of pregnancy-related deaths.
Building a Holistic Maternal Healthcare Ecosystem
To effectively tackle the maternal mortality crisis in the U.S., a holistic approach to maternal healthcare is imperative. This involves not only improving healthcare delivery systems but also addressing socioeconomic factors and social determinants of health that disproportionately affect specific populations. By creating a more inclusive healthcare environment, we can ensure better access to vital services across demographics.
Collaborative efforts between healthcare providers, policymakers, and community organizations are crucial in building an ecosystem that supports maternal health at all levels. This interconnected approach can foster resilience in maternal healthcare, ultimately leading to improved outcomes for mothers and their infants alike.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the causes of maternal mortality in the U.S. compared to other high-income countries?
Maternal mortality in the U.S. is largely attributed to a fragmented healthcare system, inequitable policies, and prevalent health disparities. Unlike other high-income nations, the U.S. faces issues like maternity care deserts and systemic biases affecting various racial and ethnic groups. These factors contribute to the high rates of pregnancy-related deaths, which remain a significant public health concern.
How do maternal health disparities impact pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S.?
Maternal health disparities in the U.S. result in stark differences in pregnancy-related deaths across racial and ethnic groups. For instance, American Indian and Alaska Native women face nearly four times the maternal mortality rate of white women. Addressing these disparities is crucial for improving overall maternal health outcomes and reducing preventable deaths during and after pregnancy.
What role does cardiovascular disease play in maternal mortality during pregnancy?
Cardiovascular disease has emerged as the leading cause of maternal mortality in the U.S., accounting for over 20% of pregnancy-related deaths. This increase is concerning as it indicates a rise in chronic conditions such as hypertension among younger individuals, highlighting the need for better prenatal care and ongoing health management during pregnancy.
How has the COVID-19 pandemic affected maternal mortality rates in the U.S.?
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted maternal mortality rates in the U.S., with a sharp increase in deaths observed during the early waves of the pandemic. Although rates decreased in subsequent years, the overall statistics from 2018 to 2022 show a worrying upward trend, reinforcing the necessity for enhanced maternal health support during crises.
What is the significance of postpartum care in reducing maternal mortality?
Postpartum care is vital for reducing maternal mortality, particularly since nearly a third of pregnancy-related deaths occur between 42 days and one year after childbirth. Shifting focus to comprehensive postpartum health can address issues that arise well past the conventional six-week recovery period, thus enhancing maternal health and reducing preventable fatalities.
Why is there a need for better tracking of maternal deaths in the U.S.?
Tracking maternal deaths in the U.S. has historically been inconsistent, complicating efforts to address and reduce pregnancy-related fatalities. The implementation of the pregnancy checkbox on death certificates has improved data collection since 2018, but a comprehensive national tracking system is still necessary to identify trends and target interventions effectively.
What actions are proposed to improve maternal health outcomes in the U.S.?
Improving maternal health outcomes in the U.S. requires increased investment in public health infrastructure, particularly in addressing state-level disparities in maternal care. Policymakers must focus on enhancing access to high-quality, full-spectrum pregnancy care and support innovative solutions designed to improve outcomes during both pregnancy and the postpartum period.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Rising Maternal Mortality Rate | The U.S. continues to have the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, with rates rising from 25.3 to 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births from 2018 to 2022. |
| Preventable Deaths | Over 80% of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. are preventable, indicating a need for better healthcare practices and policies. |
| Racial Disparities | Significant disparities exist, with American Indian and Alaska Native women experiencing a mortality rate of 106.3 per 100,000 live births compared to white women at 27.6. |
| Leading Causes of Death | Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of pregnancy-related death, reflecting a shift from hemorrhage as the primary cause. |
| Need for Better Care | Improvement is needed in prenatal and extended postpartum care to address rising rates and health disparities. |
| Structural Issues | The U.S. faces systemic issues in healthcare, including inequities in access to care, which exacerbates maternal mortality rates. |
| Investment in Public Health | There is a crucial need for increased investment in public health infrastructure to improve maternal health outcomes. |
Summary
Maternal mortality in the U.S. is a critical public health issue that continues to worsen, with significant disparities affecting certain racial groups and regions. Despite advancements, the high percentage of preventable deaths underscores the urgent need for systemic health care reforms, improved access to comprehensive prenatal and postpartum care, and targeted public health strategies to address the root causes of these tragic outcomes.