Bile imbalance liver cancer is an alarming condition that arises from disrupted bile acid production in the liver, leading to serious health consequences. Recent research highlights that this imbalance can instigate liver diseases, notably hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), which is the most prevalent form of liver cancer. A pivotal molecular switch regulating bile acids has been identified, presenting new avenues for effective liver cancer treatment. Understanding the relationship between bile acids, FXR signaling, and the YAP pathway is crucial, as their interactions can hinder bile acid homeostasis, contributing to cancer progression. By addressing these pathways, researchers aim to develop innovative therapeutic interventions that could potentially transform outcomes for patients diagnosed with bile imbalance liver cancer.
The term ‘bile imbalance liver cancer’ encapsulates the complex interplay between bile acids and liver health, particularly in relation to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Disruptions in the bile acid homeostasis, a crucial aspect of liver function, often serve as a precursor to severe liver diseases, including various forms of liver cancer. Recent studies delve into the molecular mechanisms behind this condition, revealing how aberrations in the FXR signaling and YAP pathways can exacerbate liver dysfunction and inflammation. Furthermore, understanding the role of bile acids not only enhances our grasp of liver pathology but also opens doors to potential treatments aimed at restoring balance and improving patient outcomes. By utilizing alternative terminologies related to bile metabolism and liver carcinogenesis, researchers can foster a broader dialogue about innovations in liver cancer therapy.
Understanding Bile Imbalance and Liver Cancer
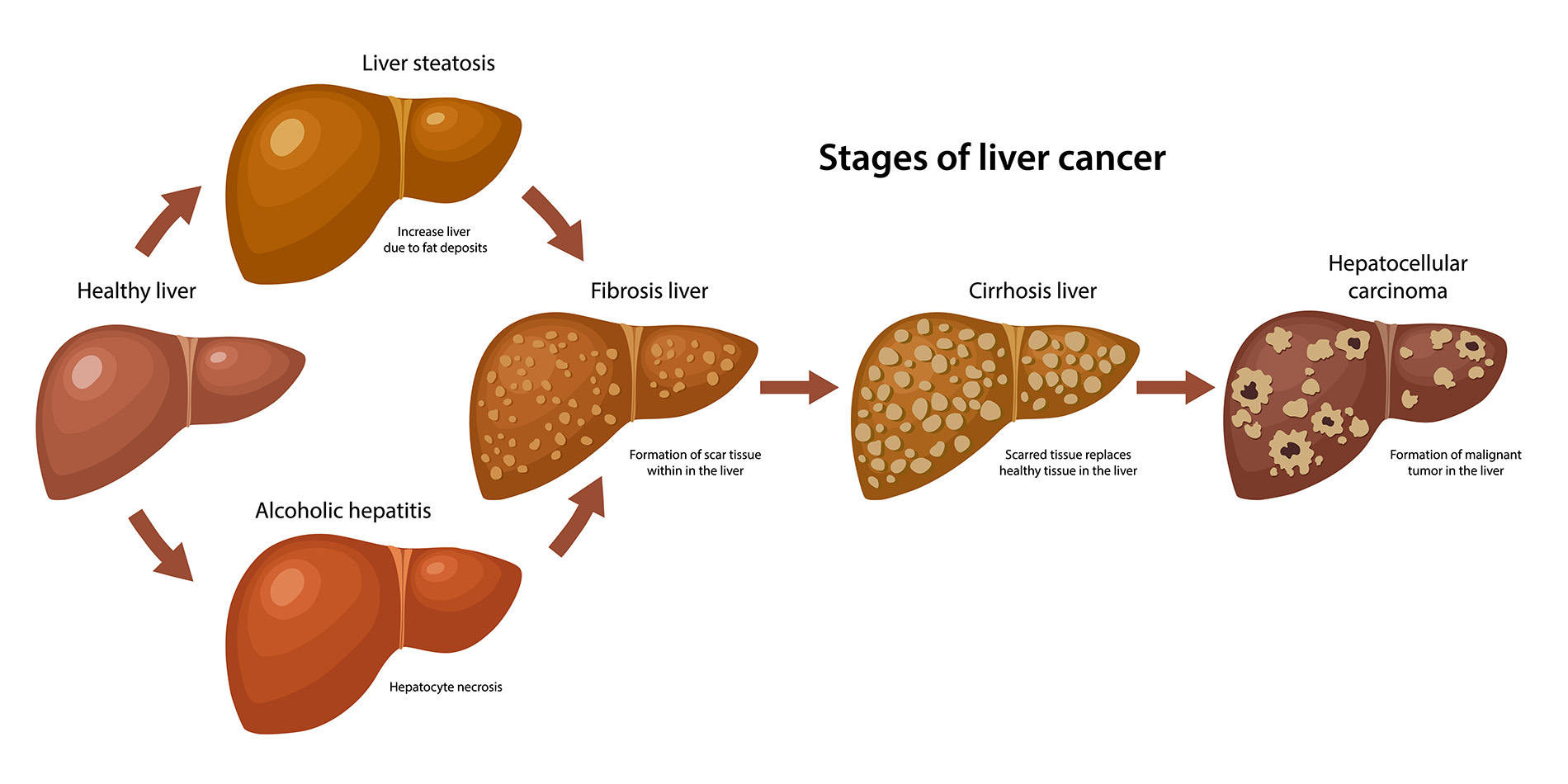
Bile imbalance is increasingly recognized as a significant factor in the development of liver diseases, including liver cancer. This is particularly relevant in the context of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), which represents the most prevalent form of liver cancer. The liver’s production of bile acids not only aids in fat digestion but also influences metabolic processes that are vital for maintaining health. When the regulated balance of bile acids is disrupted, it can lead to conditions such as liver fibrosis and inflammation, both of which are precursors to cancer development.
Recent studies indicate that altered bile acid metabolism may activate specific signaling pathways, which contribute to cancer progression. For instance, the Hippo/YAP pathway has been identified as a critical regulatory mechanism that may affect bile acid homeostasis. When this pathway is disrupted, it can lead to increased bile acid levels in the liver, further exacerbating inflammation and the risk of liver cancer. Understanding these molecular mechanisms offers crucial insights that could shape future liver cancer treatments.
The Role of FXR Signaling in Liver Health
Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) signaling plays a pivotal role in maintaining bile acid homeostasis and preventing liver disease. FXR is a nuclear receptor that regulates the synthesis and transport of bile acids, ensuring that they remain balanced within the liver. When FXR function is impaired, as occurs in cases of YAP-induced bile imbalance, bile acids can accumulate to toxic levels, resulting in liver damage and an increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. Therefore, therapies aimed at enhancing FXR activity are being explored as potential treatment options for liver-related ailments.
In experimental models, activating FXR has shown promise in mitigating liver damage caused by bile acid accumulation. Researchers have identified mechanisms to promote FXR’s function, such as through the inhibition of YAP’s repressor activity and the enhancement of bile acid excretion. These strategies may ultimately lead to innovative pharmacological approaches that harness FXR’s protective roles in liver health and could provide new avenues for preventing liver cancer.
Targeting the YAP Pathway for Liver Cancer Intervention
The YAP pathway has emerged as a key player in liver cancer development, particularly through its interaction with bile acid metabolism. As research uncovers the dual role of YAP in promoting tumor progression while simultaneously repressing FXR function, it becomes clear that targeting this pathway may offer a dual benefit in liver cancer therapy. By inhibiting YAP’s repressive activity, it may be possible to restore proper bile acid signaling and enhance FXR functions, thereby preventing liver injury and reducing cancer risk.
Scientists are investigating various methods to inhibit YAP’s oncogenic properties while allowing its physiological roles to continue. The dual targeting of bile acid metabolism and the YAP pathway represents a promising strategy to reduce the burden of hepatocellular carcinoma. As therapies become available that can effectively manipulate these signaling pathways, the potential for innovative liver cancer treatments continues to grow.
Potential Pharmacological Solutions for Bile Imbalance
Given the intricate relationship between bile imbalance and liver cancer, researchers are excited about the development of pharmacological interventions aimed at restoring this balance. Medications that target FXR signaling are under investigation, with the potential to not only facilitate proper bile acid regulation but also to mitigate the risk of developing liver cancer. These pharmacological solutions could represent a breakthrough in the treatment of liver diseases, particularly in high-risk populations.
Furthermore, the identification of compounds that can enhance bile acid export through proteins like BSEP may represent another avenue for therapeutic intervention. By promoting the excretion of excess bile acids and curbing the inflammatory processes associated with high bile acid levels, clinicians could provide a new line of defense against liver injury and cancer.
Importance of Research in Liver Biology
Research in liver biology is critical for understanding the complex mechanisms that underlie liver diseases and their links to cancer. Scholars like Yingzi Yang are at the forefront of exploring how bile acids influence metabolic processes and cell signaling pathways, such as the Hippo/YAP pathway. Their work not only sheds light on the biological underpinnings of liver cancer but also paves the way for developing targeted therapies that could transform treatment approaches.
As researchers continue to investigate the roles of bile acids and their regulatory pathways, the prospect of identifying novel therapeutic targets becomes increasingly tangible. Such efforts could lead to advancements in managing liver cancer, offering hope for patients facing these challenging diagnoses. The emphasis on interdisciplinary research helps bridge the gap between basic science and clinical application, promising a brighter future for liver health.
Nutrient Sensing and Its Impact on Liver Cancer
Nutrient sensing plays a vital role in liver function, with bile acids occupying a unique position as both digestive agents and metabolic regulators. Understanding how nutrients influence bile acid production and liver health is essential for elucidating the pathways that lead to liver cancer. Disruptions in nutrient sensing can have cascading effects, including alterations in bile acid composition that may promote tumor progression.
As emerging research links bile acids to metabolic control through pathways like FXR signaling, the significance of nutrient balance in liver health becomes more apparent. Strategies that optimize nutrient intake and enhance bile acid signaling could yield beneficial outcomes, reducing the risk of liver disease and cancer in susceptible individuals. This highlights the importance of dietary considerations and nutritional interventions in the context of liver health.
Exploring the Molecular Mechanisms of Bile Acids
Bile acids serve not only as essential components for fat digestion but also as signaling molecules that influence a variety of metabolic processes within the liver. The intricate pathways involving bile acids are vital for maintaining liver health and preventing hepatocellular carcinoma. Exploring these molecular mechanisms can reveal how disruptions can lead to pathological changes, including cancer.
Research aimed at understanding bile acid signaling pathways, such as those mediated by FXR, provides valuable insights into the etiology of liver cancer. By investigating the interactions between bile acids and other cellular pathways, scientists can develop better diagnostic and treatment strategies for liver diseases. This molecular understanding is crucial for addressing the underlying mechanisms that facilitate liver cancer progression.
Clinical Implications of Bile Acid Regulation
The clinical implications of regulating bile acids extend beyond mere digestion; they encompass the prevention and treatment of serious hepatic conditions, including liver cancer. By understanding the balance of bile acids in the body and their effects on liver physiology, healthcare professionals can better manage patients at risk for liver diseases. Such insights can lead to informed clinical decisions and targeted interventions.
The identification of molecular targets within the bile acid signaling pathway can also guide the development of specific therapies aimed at restoring homeostasis. For patients with bile acid-related liver disorders, these therapies may alleviate symptoms and prevent the progression to hepatocellular carcinoma. This represents a significant advance in liver cancer management, as it underscores the importance of a multifaceted approach to treatment.
The Future of Liver Cancer Therapy: Research and Beyond
As research continues to unveil the connections between bile imbalance and liver cancer, the future of therapy looks promising. The discovery of key molecular switches and pathways, such as FXR and YAP, opens new avenues for intervention that could significantly alter the course of liver diseases. The ongoing commitment to understanding these complex mechanisms will be fundamental in developing innovative treatment strategies.
Moreover, collaborations between research institutions and clinical settings will play a crucial role in translating scientific discoveries into patient care. As advancements in liver cancer treatment emerge, there is hope for better outcomes for patients facing this challenging disease. The integration of basic research findings into clinical practice is essential for advancing liver health and combating cancer.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the relationship between bile imbalance and liver cancer?
Bile imbalance disrupts bile acid levels in the liver, leading to inflammation and fibrosis, which can ultimately trigger hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common form of liver cancer. Elevated bile acids affect metabolic pathways related to liver cancer progression.
How do bile acids influence liver cancer treatment outcomes?
Bile acids play a crucial role in liver cancer treatment by regulating FXR signaling. When bile acids are imbalanced, it can hinder FXR’s protective functions, ultimately affecting treatment outcomes. Enhancing FXR activity may offer new therapeutic strategies for liver cancer.
What role does the YAP pathway play in bile imbalance and liver cancer?
The YAP pathway is vital in liver cancer progression, as it can suppress FXR function, resulting in bile acid overproduction. This mechanism links bile imbalance to inflammation and HCC development, demonstrating YAP’s dual role in tumor promotion.
Can liver cancer treatments focus on correcting bile acid imbalances?
Yes, liver cancer treatments could focus on correcting bile acid imbalances by targeting FXR signaling and enhancing bile acid excretion, as research suggests that restoring bile acid homeostasis may reduce liver damage and cancer progression.
What are the implications of FXR signaling in liver cancer research?
FXR signaling is vital for maintaining bile acid homeostasis. Disruption of FXR can lead to bile imbalance and contribute to liver cancer. Research into pharmacological agents that activate FXR may provide new avenues for liver cancer treatment.
How does bile acid metabolism relate to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)?
Impairments in bile acid metabolism can lead to the accumulation of toxic bile acids, causing liver inflammation and fibrosis, key factors in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Understanding this relationship may unveil new treatment targets.
What strategies may enhance bile acid export in liver cancer therapy?
Enhancing bile acid export can be a potential strategy in liver cancer therapy. This can be achieved by promoting the expression of proteins like BSEP and inhibiting pathways that disrupt bile acid transport, thereby reducing liver damage and cancer risk.
What recent findings are influencing future liver cancer treatments related to bile imbalance?
Recent findings highlight the regulatory roles of the YAP pathway and FXR in bile acid metabolism. These insights may drive the development of targeted therapies that normalize bile acid levels, potentially improving liver cancer treatment outcomes.
How could understanding bile acids improve hepatocellular carcinoma outcomes?
Improving our understanding of bile acids and their metabolic functions in liver health may lead to innovative hepatocellular carcinoma treatments that target underlying dysregulations in bile acid homeostasis, ultimately enhancing patient outcomes.
What are the primary research focuses related to bile imbalance and liver cancer?
Research primarily focuses on understanding the molecular mechanisms of bile imbalance, exploring FXR signaling and the YAP pathway, and developing targeted therapies that can restore bile acid homeostasis to prevent or treat liver cancer.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Bile Imbalance and Liver Cancer | A critical imbalance in bile acids can trigger liver diseases including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). |
| Molecular Switch | The study identified a key molecular switch that regulates bile and could lead to new treatment interventions for liver cancer. |
| Role of Bile Acids | Bile acids aid in digestion and also regulate metabolic processes, influencing liver health. |
| YAP and FXR Interaction | YAP promotes tumor formation while paralyzing FXR, leading to bile acid overproduction that causes liver damage. |
| Potential Treatments | Targeting YAP’s repressor activity or enhancing FXR function may provide new therapeutic options to prevent liver damage and cancer progression. |
| Research Background | The study was led by Yingzi Yang from Harvard, emphasizing the significance of cell signaling in liver biology and cancer. |
Summary
Bile imbalance linked to liver cancer highlights a crucial connection between bile acid regulation and the onset of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). A recent study uncovered how the disruption of bile acid homeostasis can lead to liver injury and cancer. By focusing on the molecular interactions between YAP and FXR, researchers are paving the way for innovative treatments that could enhance bile acid regulation, ultimately reducing the risk of liver cancer. This growing body of research underscores the importance of understanding bile acid metabolism in the prevention and treatment of liver diseases.