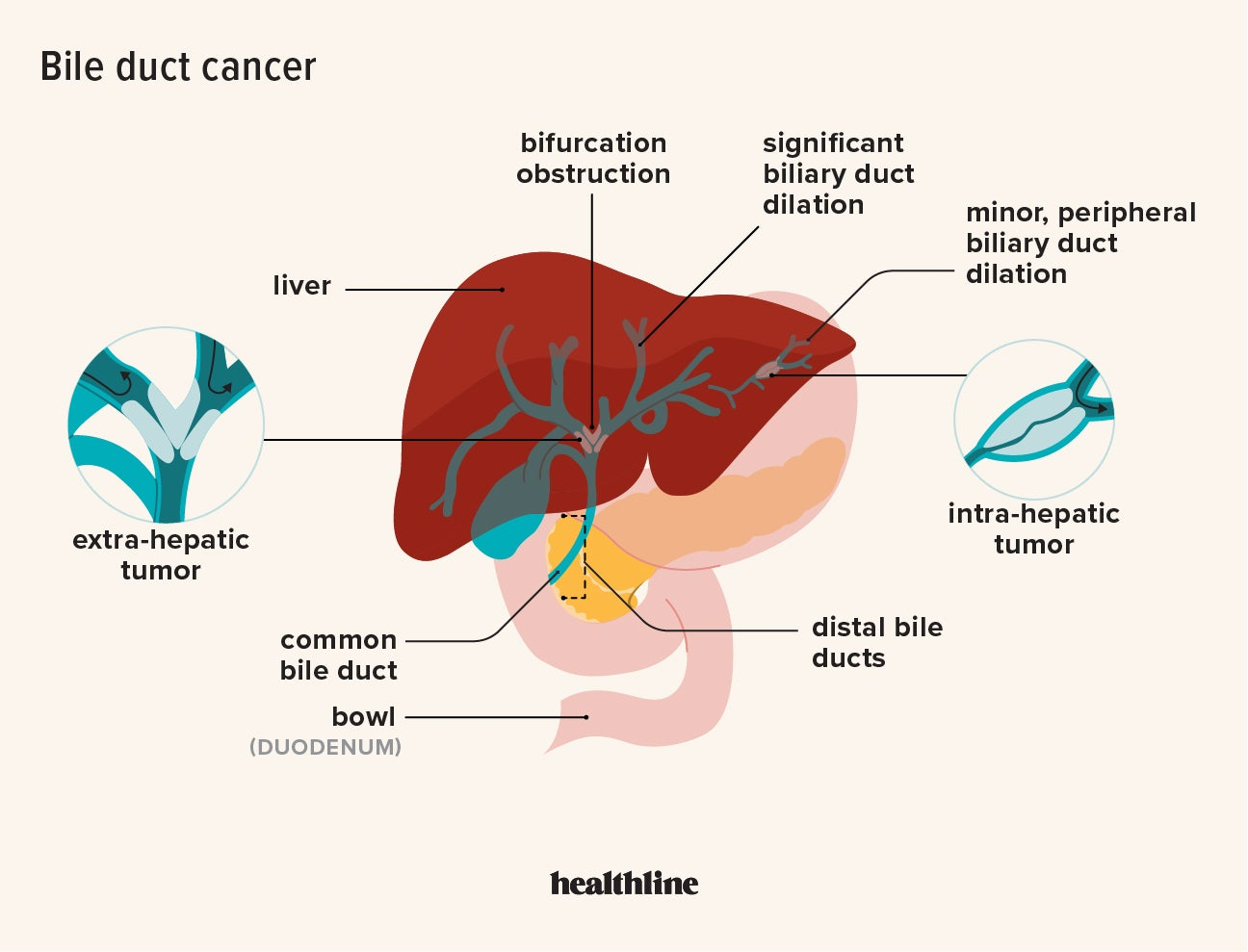
Bile imbalance and liver cancer are intricately connected, shedding light on the urgent need for enhanced liver disease research. Recent studies reveal that disruptions in bile acid metabolism can play a pivotal role in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most prevalent form of liver cancer. This research uncovers a crucial molecular switch that not only regulates bile production but also influences liver cancer treatment options. Notably, the activation of the YAP protein appears to hinder the function of the FXR receptor, further exacerbating the imbalance of bile acids. Understanding these dynamics presents new avenues for therapeutic interventions that could potentially transform outcomes for patients with liver cancer.
The relationship between bile dysregulation and hepatic malignancies is gaining increased attention in the medical community. Imbalances in biliary secretions, essential for fat digestion, can lead to severe liver conditions, prominently featuring hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Recent insights into the role of the YAP signaling pathway alongside bile acid functions underscore the complexity of liver disease. By investigating how bile acids govern metabolic processes and interact with cellular growth regulators such as FXR, researchers are paving the way for innovative liver cancer treatment strategies. This enriching discourse sheds light on the regulatory mechanisms at play in liver pathology and the potential for novel therapeutic avenues.
Understanding Bile Imbalance and Its Link to Liver Cancer
Bile imbalance plays a crucial role in the development of liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), which is recognized as the most prevalent form of liver cancer. The liver’s ability to produce bile is essential for fat digestion, but disruptions in bile acid metabolism can lead to significant health challenges. A recent study highlighted in Nature Communications has identified a key molecular switch that regulates bile production, shedding light on potential treatment interventions for liver cancer. As bile acids accumulate excessively in the liver due to this imbalance, it sets the stage for conditions such as inflammation and fibrosis, ultimately contributing to the onset of liver cancer.
The regulation of bile acids is complex, intertwining various metabolic pathways that govern liver function. Key players in this process include the YAP and FXR proteins, which have been shown to influence bile acid homeostasis and, consequently, cancer progression. Research indicates that YAP, rather than promoting growth, can repress bile acid sensing through FXR, leading to harmful bile acid overproduction. Understanding the signaling pathways involved not only enhances our knowledge of liver disease but could also pave the way for innovative therapies aimed at restoring bile balance and preventing liver cancer.
The Molecular Mechanisms of Bile Acid Metabolism
Bile acid metabolism is fundamentally tied to the health of the liver and the prevention of liver disease. FXR, the Farnesoid X receptor, plays a critical role in maintaining bile acid homeostasis, ensuring that bile production is properly regulated. An imbalance in bile acids can result in liver injury and inflammation, conditions that frequently escalate to hepatocellular carcinoma. By focusing on the molecular mechanisms governing bile acid metabolism, researchers can gain invaluable insights into the treatments available for liver cancer and potential liver disease research breakthroughs.
The Hippo/YAP signaling pathway represents an essential area of study in understanding bile acid dynamics. The interaction between YAP and FXR reveals the complexity of liver metabolism, as YAP’s capacity to inhibit FXR’s function can disrupt the delicate equilibrium of bile acids in the liver. By targeting this pathway, therapeutic options could be developed to restore the regular metabolic functions of the liver, potentially reversing or preventing the progression from liver disease to more severe conditions such as cancer.
Exploring YAP and FXR in Liver Disease Research
The interplay between YAP and FXR is at the forefront of liver disease research, as these proteins are pivotal in regulating metabolic processes that can lead to liver cancer. Recent discoveries suggest that enhancing FXR’s function or inhibiting YAP’s repressive activity could present effective strategies for combating liver disease. By targeting these proteins, researchers aim to establish pharmacological solutions that could mitigate liver damage and stave off the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Understanding how YAP influences metabolic control expands the horizon of liver research significantly. As scholars like Yingzi Yang delve into this intricate web of cellular signaling, they open pathways for innovative therapies aimed at liver diseases. The findings emphasize the importance of continued research into bile acid metabolism and the potential for discovering new treatments that could change the landscape of liver cancer care.
Innovations in Liver Cancer Treatment
The key findings on bile acid imbalance and its implications for liver cancer treatment are groundbreaking. With the identification of how YAP represses FXR function, a new avenue has opened for developing targeted therapies that can enhance bile acid excretion and prevent liver cancer progression. This line of research not only adds to existing knowledge but also sets the stage for clinical applications that could transform patient outcomes.
Innovations in liver cancer treatment stemming from these studies may involve pharmacological interventions aimed at stimulating FXR or utilizing gene therapies to inhibit YAP. Such advances could mitigate liver damage caused by bile acid imbalances and effectively reduce the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma. As researchers continue to explore these potential treatments, the future of liver disease management looks promising.
Bile Acid Dynamics and Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Understanding bile acid dynamics is essential, especially when discussing conditions such as hepatocellular carcinoma. The liver’s production of bile acids is not just a matter of digestion; it is a critical regulatory function, influencing various metabolic processes and liver health. Disruption in this dynamic can lead to severe consequences, including an increased risk of liver cancer. Research has unearthed the link between bile acid homeostasis and tumor formation, showing that maintaining balance is crucial for preventing diseases.
Investigations into how dysregulated bile acids activate pathways leading to hepatocellular carcinoma have significant implications for liver disease research. By further exploring these links and the role of factors like YAP and FXR, scientists are paving the way for potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets that could significantly alter the landscape of treatment for liver cancer.
Prevention Strategies for Liver Disease
Prevention strategies for liver disease are becoming increasingly focused on the regulation of bile acid metabolism. By understanding how bile acids contribute to liver injury and inflammation, healthcare professionals can develop comprehensive prevention protocols. This includes lifestyle recommendations, dietary changes, and monitoring bile acid levels to prevent liver diseases from escalating into more severe conditions like hepatocellular carcinoma.
Furthermore, the implementation of preventative measures based on research findings regarding YAP and FXR allows for a more proactive approach. As treatments and guidelines evolve, this understanding can lead to better patient outcomes by reducing the overall incidence of liver diseases linked to bile acid imbalance.
Future Directions in Liver Cancer Research
The future directions in liver cancer research are promising, as studies continue to unravel the complexities of bile acid metabolism and its connection to hepatocellular carcinoma. With identified pathways and molecular switches like YAP and FXR, researchers are poised to explore new therapeutic interventions that could reshape treatment protocols for liver cancer. This focus provides hope for improved outcomes through early interventions and personalized medicine.
As the field of liver disease research advances, the integration of genetic and genomic techniques will likely play a significant role. Future research initiatives may leverage these tools to illuminate the pathways underlying bile acid dysregulation and liver cancer development, paving the way for innovative and targeted therapies that are both effective and practical in clinical settings.
The Role of Nutrition in Liver Health
Nutrition plays a vital role in maintaining liver health and preventing conditions associated with bile acid imbalance. Proper dietary choices can support liver function, reduce inflammation, and optimize bile acid metabolism, which is essential for digestive health. Understanding the relationship between nutrition and liver diseases provides valuable insights into how lifestyle modifications can aid in preventing hepatocellular carcinoma, especially for individuals at risk.
Research suggests that specific nutrients and dietary patterns may influence bile acid production and metabolism. A diet low in refined sugars and high in whole foods can promote a healthier liver environment, potentially lowering the risk of liver diseases. Continuous nutritional research will be essential in developing targeted interventions that bolster liver health and enhance overall metabolic function.
Molecular Targets for Innovative Liver Cancer Therapies
Identifying molecular targets for liver cancer therapies has gained momentum with discoveries relating to bile acid metabolism. The roles of YAP and FXR provide key insights into potential therapeutic strategies to combat hepatocellular carcinoma. Researchers are now exploring inhibitors that may activate FXR or suppress YAP to reinstate the balance of bile acids and subsequently mitigate liver damage.
This innovative approach not only holds promise for improving treatment outcomes but could also transform preventative measures against liver cancer. By focusing on molecular targets, therapy can be personalized according to the individual metabolic landscape, enabling a more tailored approach to liver disease management and opening doors to new avenues of research and development in cancer therapies.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is bile imbalance related to liver cancer?
Bile imbalance is closely linked to liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). A study revealed that disruption in bile acid metabolism can cause liver injury and inflammation, ultimately leading to the development of liver cancer. The overproduction and accumulation of bile acids in the liver due to this imbalance promote tumor formation.
What role do YAP and FXR play in bile acid metabolism and liver cancer?
YAP (Yes-associated protein) and FXR (Farnesoid X receptor) are crucial in regulating bile acid metabolism. YAP acts as a repressor that inhibits FXR’s role in maintaining bile acid homeostasis, causing an overproduction of bile acids. This accumulation contributes to liver inflammation and cancer development, making YAP and FXR critical targets for liver cancer treatment.
What are potential liver cancer treatments targeting bile acid pathways?
Potential liver cancer treatments may focus on enhancing FXR function or promoting bile acid excretion to counteract the effects of YAP activation. Researchers are exploring pharmacological solutions that stimulate FXR activity, which could mitigate liver damage and reduce cancer progression by restoring normal bile acid metabolism.
What does recent liver disease research reveal about hepatoceullar carcinoma?
Recent liver disease research emphasizes the importance of bile imbalance in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Studies indicate that regulating bile acid metabolism is essential to prevent liver damage and inflammation, which are precursors to cancer. Understanding these mechanisms can inform future liver cancer treatment strategies.
How does bile acid accumulation lead to liver cancer?
Bile acid accumulation leads to liver cancer primarily through its inflammatory effects. When bile acids are overproduced due to regulatory imbalances, they can cause fibrosis and inflammation in the liver tissue. Over time, this chronic injury can initiate the processes that result in hepatocellular carcinoma, the most common type of liver cancer.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Bile Imbalance and Liver Cancer | A critical imbalance in bile acids is linked to liver diseases, especially hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most prevalent type of liver cancer. |
| Key Molecular Switch Identified | The study identifies a key molecular switch involved in bile regulation, providing insights into potential treatment options. |
| Role of YAP in Bile Metabolism | YAP, a crucial component of the Hippo pathway, acts as a repressor affecting bile acid metabolism and contributing to liver damage. |
| Impact of FXR | The Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) is essential for bile acid homeostasis. YAP’s interference with FXR leads to bile accumulation and liver cancer. |
| Potential Treatment Innovations | Enhancing FXR function and promoting bile acid excretion may provide new therapeutic strategies to combat liver damage and cancer progression. |
Summary
Bile imbalance and liver cancer are intricately connected, as revealed by recent research which highlights how disruptions in bile acid regulation can lead to severe liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The study uncovers a key molecular switch that could pave the way for new treatment avenues by targeting specific pathways involved in bile metabolism. Understanding the roles of YAP and FXR provides valuable insights necessary for developing effective therapeutic strategies against liver cancer, offering hope for improved patient outcomes.