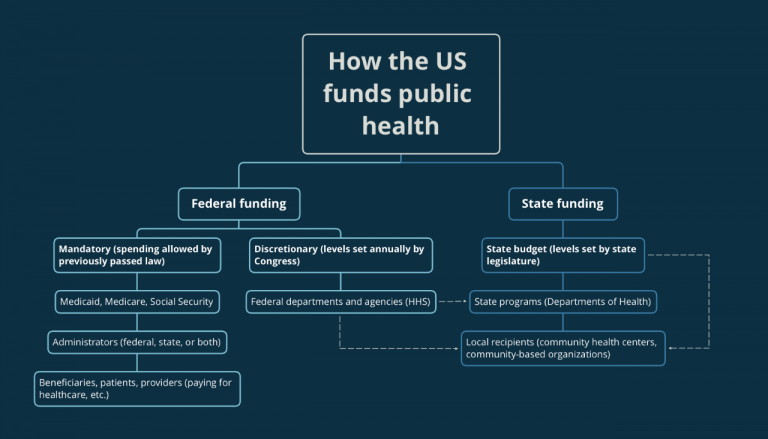
Federal grants in public health play a crucial role in advancing our understanding and strategies for improving health outcomes across populations. These grants, facilitated by various governmental agencies like the National Institutes of Health (NIH), provide essential federal funding for research that addresses pressing health challenges, including cancer risk reduction and nutritional epidemiology. Researchers like Karen Emmons and Jorge Chavarro rely on these grants not only to explore innovative scientific inquiries, but also to build community partnerships that enhance the public health landscape. The process of securing these competitive funds involves navigating the NIH grant application process, which emphasizes rigor and relevance in the proposed research. As such, federal grants in public health are not just financial resources; they are lifelines that empower researchers to make significant contributions to public health research and interventions.
In the realm of public health improvement, government-sponsored funding initiatives are vital for supporting innovative health studies and interventions. Researchers are often on the lookout for federal resources that can bolster their investigative efforts, particularly in fields like cancer prevention and dietary health. The intricacies of obtaining these funds involve navigating a meticulous application process that ensures only the most promising research projects receive backing. As healthcare challenges continue to evolve, securing these funds becomes crucial for advancing knowledge and practices that could lead to healthier communities. Ultimately, this government support not only fuels academic research but also fosters public welfare by addressing the medical concerns of our time.
The Impact of Federal Grants in Public Health Research
Federal grants play a critical role in advancing public health research, enabling scientists to explore new methodologies and treatment strategies that ultimately aim to improve community health outcomes. For instance, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) provides substantial funding that supports studies focused on cancer risk reduction and nutritional epidemiology. Such funding opportunities empower researchers like Karen Emmons and Jorge Chavarro, who translate their academic expertise into practical interventions aimed at mitigating health disparities. As they navigate the complex landscape of grant applications, the emphasis placed on innovation and relevance to public health ensures that the research carries a meaningful impact on society.
However, the acquisition of federal grants isn’t merely a formality; it requires meticulous planning and a well-crafted proposal. Researchers must demonstrate the significance of their work, aligning their goals with federal health priorities while showcasing how their project addresses urgent public health needs. This competitive process also underscores the importance of collaboration with community partners, as fostering these relationships helps ensure that the research is both applicable and beneficial to the populations it aims to serve. In an era where public health challenges are more pressing than ever, securing federal funding enables researchers to make strategic advances that resonate with current health policies.
Navigating the NIH Grant Application Process
The NIH grant application process is renowned for its rigor and complexity, requiring applicants to meticulously outline their research proposals in comprehensive detail. Initially, researchers must draft a one-page specific aims document, highlighting how their study fills existing knowledge gaps and its potential implications for public health. This initial summary sets the stage for a more extensive application, which may extend well beyond 100 pages, incorporating detailed methodologies, preliminary research findings, and ethical considerations, especially when involving human subjects. The thoroughness expected in these proposals underscores the high stakes associated with federal funding, as the quality of submissions directly influences funding success rates.
Evaluators within the NIH exhibit a commitment to fair assessment, utilizing a system that scores proposals based on criteria such as innovation, significance, and methodology. The competitive nature of the review process means that researchers face harsh realities, with success rates often falling below 20%, especially at institutions like the National Cancer Institute. Despite the challenges inherent in this process, both Chavarro and Emmons find value in the stringent reviews as they cultivate high standards for scientific inquiry. The feedback provided for proposals that do not secure funding is critical, offering insights that can enhance future applications and foster continued growth in public health research.
Building Collaborative Relationships for Better Outcomes
The journey toward securing federal grants in public health research extends well beyond the application itself; it necessitates building collaborative relationships with community stakeholders. Emmons’ emphasis on partnerships highlights the importance of engaging with populations directly impacted by public health concerns. By fostering these relationships, researchers can develop studies that are more attuned to the needs of the communities they aim to assist, thus ensuring their findings translate into actionable interventions. This collaborative approach not only strengthens research proposals but also fosters trust between researchers and community members, facilitating more effective dissemination of public health knowledge.
Moreover, these partnerships create a feedback loop that enhances the relevance and applicability of research findings. Researchers who involve community members in the design and implementation of their projects are more likely to address issues that resonate with those populations, enhancing both the ethical considerations and practical impacts of their work. As public health research becomes increasingly intertwined with community engagement, it underscores the necessity for scientists to act as not only investigators but as advocates for the welfare of the communities they serve. This shift can lead to more sustainable public health outcomes and greater societal benefit.
Ethical Considerations in Public Health Research
Ethical considerations form an essential component of public health research, particularly when human subjects are involved. Researchers like Emmons must navigate a labyrinth of regulations aimed at protecting participants, which not only includes ensuring informed consent but also addressing potential risks associated with their studies. The NIH emphasizes a commitment to the ethical treatment of research participants, which must be meticulously documented in grant applications. As researchers draft their proposals, it becomes crucial to demonstrate how they plan to safeguard the rights and welfare of individuals contributing to their studies, as these ethical frameworks are paramount in gaining approval from funding bodies.
The ethical responsibilities extend beyond compliance with regulatory requirements; they also involve a moral obligation to produce research that genuinely benefits participants and the broader community. This aspect of ethical research heightens the stakes for public health researchers, as they must consistently consider the implications of their findings. Emmons’ approach emphasizes that successful research should not only advance scientific knowledge but should also deliver tangible benefits to the populations in question. As public health challenges continue to evolve, a strong ethical foundation remains imperative in fostering trust, enhancing collaboration, and ultimately driving positive health outcomes.
The Role of Federal Funding in Advancing Public Health Initiatives
Federal funding is indispensable for advancing public health initiatives, as it lays the groundwork for a variety of research projects aimed at tackling pressing health challenges. The NIH plays a crucial role in this ecosystem, offering grants that fuel studies on critical issues such as cancer prevention and nutritional epidemiology. By providing financial resources, federal funding enables researchers to explore innovative solutions, ensuring that public health strategies are informed by the latest scientific knowledge and evidence-based practices. This funding stream not only accumulates a wealth of data but also supports initiatives that can transform health policy and practice on a national scale.
Moreover, the impact of federal grants extends beyond individual research projects. They contribute to the establishment of robust public health infrastructures, fostering collaboration between academic institutions, governmental agencies, and community organizations. Such partnerships enhance knowledge sharing and resource pooling, ultimately leading to improved health outcomes. As researchers like Emmons advocate for well-designed health interventions in under-resourced communities, federal funding serves as a linchpin for implementing strategies that address health inequities, reduce disease risk, and promote overall wellness in diverse populations.
The Five-phase Framework for Grant Writing Success
Successful grant writing in public health research can be boiled down to a five-phase framework that guides researchers through the intricate process of obtaining funding. The first phase involves comprehensive preparation, which includes identifying a relevant research problem, reviewing the literature for existing studies, and establishing partnerships with community stakeholders. In this phase, researchers must ensure that their proposed study aligns with federal health priorities and addresses pressing public health needs. By investing time upfront in preparation and networking, grant applicants set a strong foundation for a compelling proposal that speaks directly to the objectives of funding bodies.
The subsequent phases involve drafting the grant application, incorporating feedback, submission, and revising based on reviewer comments. While the writing phase demands attention to detail and adherence to specific formatting requirements, it also calls for articulation of the potential impact of the research on public health. Emphasizing the significance of the study and its innovative aspects is vital to capturing the attention of funding reviewers. This structured approach not only streamlines the grant application process but also maximizes the chances of securing federal funding necessary for advancing public health initiatives.
Leveraging Pilot Studies to Strengthen Grant Proposals
Incorporating pilot studies can significantly enhance the competitiveness of grant proposals in public health research. Pilot studies allow researchers to gather preliminary data that can substantiate the feasibility and potential impact of larger research projects. By demonstrating that a proposed intervention or study design has been tested with a smaller cohort, researchers can address potential reviewers’ concerns about the viability of their initiatives. Such evidence is often crucial for funding bodies, as it not only showcases innovation but also helps to build a stronger rationale for the study’s objectives.
Additionally, results from pilot studies can provide insights into methodological adjustments needed for the larger project, allowing researchers to refine their approach. Reporting pilot outcomes can demonstrate to grant reviewers the researcher’s commitment to thoroughness and attention to detail—qualities that are highly valued in the NIH grant application process. By leveraging pilot studies effectively, public health researchers can not only bolster their chances of obtaining federal funding but also increase the overall quality and reliability of their research outcomes.
Community Engagement: Essential for Successful Public Health Research
Community engagement is a fundamental aspect of public health research that cannot be overstated. Engaging communities in the research process fosters transparency and ensures that studies are truly reflective of the populations they aim to serve. Involving community members as collaborators rather than merely subjects can yield valuable insights that enhance the relevance and applicability of health interventions. Researchers like Emmons actively seek feedback from local communities when designing their studies, which helps align research objectives with community needs and cultural considerations.
Furthermore, effective community engagement promotes trust and buy-in, which can ultimately improve participant recruitment and retention in studies. When communities feel included in the process, they are more likely to support the research and contribute to its success. Researchers are often reminded that their work should transcend academia and lead to actionable benefits for those they study. By placing a strong emphasis on collaboration and community input, public health researchers can facilitate a more ethical and impactful research trajectory that addresses significant health disparities.
Challenges and Opportunities in Federal Grant Funding
The landscape of federal grant funding for public health research is rife with challenges, particularly in the context of shifting political climates and economic constraints. Recent attempts by various administrations to freeze or redirect funding have raised concerns among researchers about the viability of their work. Researchers like Emmons have found themselves navigating not only the complexities of the grant application process but also the wider implications of policy changes that can disrupt ongoing studies. The uncertainty surrounding federal funding amplifies the stakes associated with grant proposals and underscores the need for clear communication between institutions and policymakers.
Despite these challenges, opportunities remain for public health researchers to advocate for sustained funding and support for their work. Engaging in dialogue with funding agencies and demonstrating the importance of their research can help secure necessary resources. Researchers are called upon to not only seek grants but also to champion public health initiatives that demonstrate tangible benefits, thereby advocating for a commitment to funding that prioritizes health advancements. By continuously pressing for funding support and showcasing the impact of their research, public health scientists can help ensure a stable future for both their studies and the communities they serve.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are federal grants in public health and how do they support research?
Federal grants in public health are financial awards provided by government agencies, such as the NIH, to fund research projects aimed at improving public health outcomes. These grants support various initiatives, including public health research focused on cancer risk reduction and nutritional epidemiology, allowing scientists to investigate preventive measures, develop interventions, and disseminate findings that can significantly impact community health.
How can I apply for federal funding for research in public health?
To apply for federal funding for research in public health, researchers must follow the NIH grant application process. This typically involves identifying a relevant funding opportunity, developing a clear research proposal that addresses key public health issues, preparing a detailed budget, and submitting the application through the appropriate channels. Successful grants usually demonstrate innovation, significance, feasibility, and thorough methodology.
What is the success rate for NIH grant applications in public health research?
The success rate for NIH grant applications varies by institute and funding mechanism. For example, the National Cancer Institute reported a success rate of 14.6 percent for the R01 grants in 2023. This indicates that despite rigorous preparation, only a small fraction of proposals in public health research secures funding, emphasizing the competitive nature of federal grants.
What factors contribute to securing federal grants in public health?
Securing federal grants in public health depends on several factors, including the quality and innovation of the research proposal, the significance and impact of the study on public health challenges, a well-justified budget, and adherence to ethical standards in research methodologies. Collaboration with community partners and previous research experience also enhance the chances of grant success.
Why are federal grants essential for public health research initiatives?
Federal grants are essential for public health research initiatives because they provide necessary funding that supports innovative research aimed at addressing pressing health issues, such as cancer risk reduction and promoting healthier populations. These grants not only facilitate scientific discovery but also ensure that critical public health interventions can be developed and implemented effectively.
What types of public health research are most commonly funded by federal grants?
Federal grants commonly fund a wide range of public health research areas, including cancer risk reduction, epidemiological studies on nutrition (nutritional epidemiology), mental health interventions, and the effectiveness of community health programs. Research proposals that address significant public health challenges and demonstrate potential for impactful outcomes are prioritized.
How does the NIH grant application process work for public health research?
The NIH grant application process for public health research involves several key steps: first, researchers must identify funding opportunities, then formulate specific aims outlining their research goals. Following that, they prepare a comprehensive application that details methodology, expected outcomes, and a budget. After submission, the application undergoes rigorous peer review by scientific review groups, with the highest-rated proposals advancing for funding consideration.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Research in public health, particularly by Karen Emmons and Jorge Chavarro, focuses on reducing cancer risk and nutrition’s impact on reproduction. |
| Federal grants are crucial for funding essential research projects and advancing public health initiatives. |
| The grant application process is lengthy and competitive, requiring detailed proposals and budgeting. |
| Success rates for grant proposals are low; for instance, only 14.6% of R01 grants were funded at the National Cancer Institute in 2023. |
| Researchers can resubmit unsuccessful applications based on feedback, fostering continuous improvement and innovation in research. |
| The collaboration between government and public health institutions emphasizes the societal benefits of scientific research. |
Summary
Federal grants in public health are essential for empowering researchers to address critical health issues such as cancer and nutrition. The rigorous process of applying for these grants, illustrated by the experiences of researchers like Karen Emmons and Jorge Chavarro, highlights the dedication required to secure funding. Despite current challenges and low success rates, the collaborative efforts between public health institutions and the government underscore the commitment to enhancing public health outcomes. Through these federal grants, scientists can maintain the momentum needed to innovate and ultimately improve the health of communities.