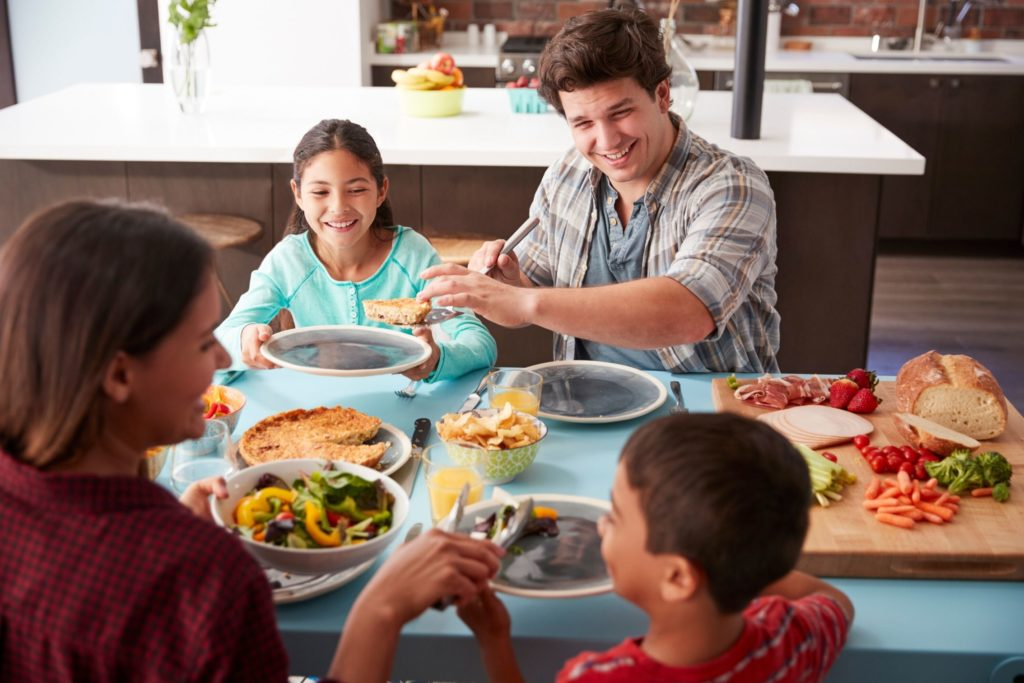
Shared meals and happiness are intricately intertwined, revealing profound insights into our well-being. Studies indicate that eating together not only boosts satisfaction but also fosters positive emotions, making communal dining a celebrated ritual. In fact, research has shown that the frequency of shared meals serves as a strong predictor of happiness, sometimes surpassing income as an indicator of life satisfaction. As modern society trends toward solitary dining, it’s crucial to recognize how meal sharing enhances social connections and contributes to well-being indicators. Embracing the benefits of meal sharing may be a simple yet powerful step toward fostering happiness in our lives.
The delightful act of gathering around a table to enjoy food can significantly enhance our sense of joy and fulfillment. This phenomenon of communal dining, often described as a catalyst for positive relationships and emotional well-being, highlights the importance of social interactions during meals. When friends and family come together to savor a meal, they create lasting memories, reinforcing bonds that contribute to overall happiness. As recent happiness studies have pointed out, the social aspect of eating is as vital to our quality of life as financial stability. Thus, understanding the value of dining together can reshape our perspective on social connections and personal contentment.
The Profound Impact of Shared Meals on Happiness
Shared meals carry immense psychological benefits that go beyond simple nourishment. Studies indicate that eating together is often linked to stronger social connections, as the act of sharing food fosters a sense of community and belonging. This communal aspect is aligned with well-being indicators; individuals who frequently dine with family and friends report higher levels of life satisfaction. These social interactions during meals are essential, suggesting that they can significantly contribute to one’s overall happiness, making shared dining not merely a routine but a vital component of mental well-being.
Moreover, happiness studies emphasize that those who partake in shared meals tend to express more positive emotions and life satisfaction. The intimate nature of being around others when eating alleviates feelings of loneliness and isolation that many face today. This correlation suggests that fostering environments where shared meals are encouraged could lead to a happier, more fulfilled society. As we navigate the complexities of modern living, recognizing these meal-sharing benefits becomes crucial for enhancing social bonds and individual happiness.
The Decline of Dining Together: A Warning Signal
Despite the clear connection between shared meals and happiness, recent data shows a troubling trend: an increasing number of people are eating alone. According to the American Time Use Survey, more than 25% of Americans reported dining independently, marking a significant rise over the past two decades. This shift is particularly pronounced among younger demographics, who are essential to fostering future social connections. The implications of this trend are profound, suggesting that rising social isolation may simultaneously contribute to diminishing happiness levels.
As we face challenges related to mental health and social well-being, the decline of meal sharing represents a potential crisis in our societal fabric. The act of eating together not only enhances personal joy but also strengthens communities by building networks of support and friendship. It is vital for policymakers to address this issue proactively. Encouraging communal meals through community programs and social initiatives can help reverse this trend, promoting both the joy of shared experiences and overall mental health in society.
Implications for Policymaking: Prioritizing Meal Sharing in Communities
The relationship between shared meals and happiness presents critical insights for policymakers aiming to enhance community well-being. By understanding that eating together is a substantial indicator of social connection, initiatives can be designed to promote communal dining experiences. Such measures might include organizing regular community dinners or establishing neighborhood potlucks, which could effectively combat social isolation by bringing residents together, fostering friendship, and creating supportive networks.
Furthermore, incorporating meal-sharing programs in schools and workplaces could instill the importance of social interactions at an early age. Schools can create lunch programs that encourage group dining, while workplaces can develop lunch and learn sessions that allow employees to bond over shared meals. By embedding the practice of eating together into various spheres of life, we can create a sense of belonging and support, reinforcing the idea that shared meals are vital not only for individual happiness but also for community resilience.
Causal Relationships: Do Shared Meals Lead to Greater Happiness?
While numerous studies have demonstrated a strong correlation between shared meals and happiness, the question of causation remains partially unresolved. It is a fascinating area for future research to ascertain if individuals become happier as they engage more frequently in shared dining experiences or if inherently happier individuals are simply more inclined to share meals. The complexity of these interactions is further compounded by the diverse factors that contribute to a person’s overall happiness.
Understanding the dynamics of these relationships could offer invaluable insight into enhancing well-being strategies. If future research identifies shared meals as a direct contributor to increased happiness, it would reinforce the necessity for societal shifts towards communal dining. This paradigm shift would not only elevate individual cases of happiness but also foster a broader culture of support and cohesion across communities.
Physical Health Benefits of Eating Together
In addition to mental health benefits, shared meals frequently lead to improvements in physical health. Eating together often encourages healthier eating habits, where individuals choose more nutritious foods and portion sizes are typically more moderated. Families that prioritize shared meals are less likely to indulge in unhealthy snacking. Consequently, this collective approach to dining contributes positively to physical well-being, reinforcing the overall sense of happiness that accompanies improved health.
Moreover, research indicates that communal dining can reduce the risk of obesity and associated health issues, as individuals are more likely to engage in healthier eating behaviors when in the presence of others. The supportive environment nurtured during meal sharing may encourage individuals to make better dietary choices, underscoring how shared meals can potentially enhance both physical health outcomes and happiness levels.
The Role of Cultural Practices in Meal Sharing
Cultural practices play a pivotal role in how shared meals are perceived and conducted across different societies. Many cultures have traditional rituals surrounding dining that foster social ties, whether it’s the Sunday family dinner or festive holidays where large gatherings are commonplace. These practices instill a sense of belonging and identity, reinforcing social connections that impact happiness. By valuing and perpetuating cultural meal-sharing traditions, communities can uplift collective happiness and connection.
Furthermore, exploring global perspectives on meal sharing reveals diverse methods of fostering joy and togetherness. For example, the Mediterranean countries emphasize communal dining practices that celebrate both food and social interaction, which correlate strongly with higher reported happiness levels. Understanding these cultural dimensions can help inform practices in societies experiencing social isolation, pointing towards effective strategies that promote shared meals as a pathway to enhanced well-being.
Establishing Community Policies for Shared Meals
As evidence mounts regarding the importance of shared meals for enhancing happiness, it’s imperative for local governments and organizations to develop policies that encourage these gatherings. Community kitchens, farmers’ markets with communal feeding areas, and organized meal-sharing events are all effective initiatives that can be implemented. Such programs can significantly boost social interactions among residents, thereby fostering a stronger community fabric conducive to elevated happiness levels.
Additionally, policy measures could focus on collaborations with local businesses to support initiatives that facilitate meal sharing. Providing incentives for restaurants to offer communal dining options or discounts for families dining together can further encourage people to seek shared experiences around food. By embedding the practice of eating together into community planning, we cultivate environments that prioritize social connections and heighten individual and collective well-being.
Encouraging Families to Share Meals: Practical Tips
Encouraging families to incorporate shared meal times can be as simple as establishing ‘family time’ at dinner. Setting aside dedicated times for family meals creates a routine that reinforces the importance of dining together. Preparing meals together can also enhance bonding, as family members engage in cooperative activities, making shared meals a form of togetherness that nurtures connection.
Incorporating discussions or activities during meal times can further enhance the experience, making it a time for connection and sharing stories. Families can utilize this time to engage in meaningful conversations, discuss their day, and even establish family traditions, all of which contribute positively to individual happiness and strengthen familial bonds. By prioritizing shared meals as a family practice, we can bolster social connections and improve overall well-being.
Findings from Happiness Studies: Insights into Meal Sharing
Happiness studies have extensively documented the benefits of shared meals, showing a remarkable correlation between dining together and increased happiness levels. Researchers have found that individuals who regularly share meals report higher life satisfaction and emotional well-being. These insights emphasize that beyond physical nourishment, shared meals serve as a social glue, enhancing connections that enrich emotional experiences.
In exploring various happiness measures, it’s evident that shared dining experiences significantly contribute to positive emotional outcomes. Understanding the dynamics of happy communities often leads back to the act of eating together. By championing meal sharing as a community hallmark rather than an individual affair, societies can cultivate environments where happiness proliferates, creating a collective ethos of joy and connection.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the benefits of shared meals for happiness?
Shared meals have been linked to increased happiness and well-being. Research indicates that individuals who dine with others report higher life satisfaction and positive emotions, making meal sharing a crucial factor in enhancing social connections and overall happiness.
How do happiness studies relate to shared meals?
Happiness studies, including findings from the World Happiness Report, show that the frequency of shared meals correlates strongly with happiness levels across various demographics. This suggests that eating together can serve as a reliable well-being indicator, potentially even more so than financial status.
Why is eating together important for social connections?
Eating together fosters social connections by creating opportunities for interaction, bonding, and shared experiences. These shared meals not only enhance relationships but also serve as a vital part of community life that contributes to individual happiness.
What role do shared meals play in well-being indicators?
Shared meals are considered one of the key well-being indicators in research studies. They provide measurable insights into social interactions, as the frequency of dining with others is closely linked to higher reported happiness, suggesting that these meals are integral to both personal and communal well-being.
Can shared meals improve mental health?
Yes, shared meals can significantly improve mental health. By promoting socialization and reducing feelings of loneliness, eating together can enhance emotional well-being and potentially mitigate issues related to mental health, making it an essential practice for fostering positive emotional states.
How can I incorporate more shared meals into my life for happiness?
To incorporate more shared meals and boost happiness, consider inviting friends or family over more often, participating in community dinners, or even scheduling regular meals with colleagues. Making dining an interactive and group-oriented activity can help strengthen social bonds and contribute to greater overall happiness.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Shared Meals and Happiness | Shared meals are a strong predictor of happiness, potentially more so than factors like income or employment. |
| Increasing Trend of Eating Alone | Recent statistics show a significant rise in Americans dining alone, with 1 in 4 reporting eating all meals alone, an increase of 53% since 2003. |
| Importance of Shared Meals | The study emphasizes that the number of shared meals may offer clearer insights into well-being than traditional measures like income. |
| Future Research Directions | Further research aims to determine whether sharing meals leads to increased happiness or if happier people are more inclined to share meals. |
| Policy Implications | Encouraging shared meals could be a strategy for improving mental health and social connectivity in communities. |
Summary
Shared meals and happiness are intricately linked, as suggested by recent research indicating that the frequency of meals shared with others is a strong indicator of overall well-being. The study highlights a troubling trend of increasing solitary dining among Americans, which correlates with declining happiness levels. Understanding this relationship emphasizes the importance of communal eating as a potential intervention strategy for better mental health and social cohesion. By promoting shared meals, we could foster greater happiness and community connection.